How to publish from release pipeline in azure devops
Published:
How to publish from Release Pipeline in Azure DevOps


In this section, I shall describe how you can get the artifact from the release pipeline,
Publishing any artifact from the build pipeline is pretty easy and there are plenty of tutorials available on the internet,
To publish an artifact from a build pipeline in Azure DevOps, you can use the Publish Build Artifacts task. Here’s how you can do it:
- In your build pipeline, add the
Publish Build Artifactstask to a phase that runs after the build is completed. - In the
Path to publishfield, specify the path to the folder that contains the artifacts you want to publish. You can use a wildcard pattern to include multiple files and folders. - In the
Artifact namefield, enter a name for the artifact. - In the
Artifact publish locationfield, choose whether you want to publish the artifact to the pipeline or to a file share. - If you are publishing to a file share, enter the path to the share in the
Path to publish on the serverfield. - Save and run your pipeline.
That’s it! The Publish Build Artifacts task will publish the specified artifacts to the pipeline or file share you specified. You can then use the artifact in a release pipeline or download it from the Artifacts page in Azure DevOps.
- task: PublishPipelineArtifact@1
displayName: 'Publish Pipeline Artifact'
inputs:
targetPath: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)'
artifact: drop
Now for any reason, you may want to get the same result from the release pipeline as well, but unfortunately, the PublishPipelineArtifact@1 task does not support in release pipeline and even if you run it you will get some error, to solve this you can do one thing,
Pushing the artifact in a git repo
in this way essentially you can save the copy of your updated artifacts in a separate folder inside your git repo.
let me show my scenario,
we are following the git flow branching strategy, so as you can see in each environment we need to save a copy of the updated ARM template .
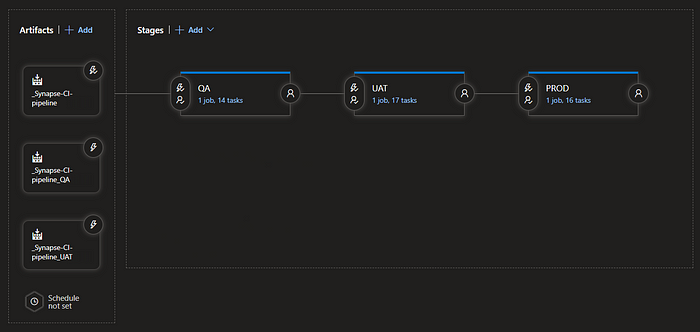
How did I achieve this?
Well, let me guide you step by step.
First, give all the permission required so that the pipeline can access the repo and push to it!
Go to project settings → Repository → select your repo →security → project collection Administrators → contribute → ALLOW
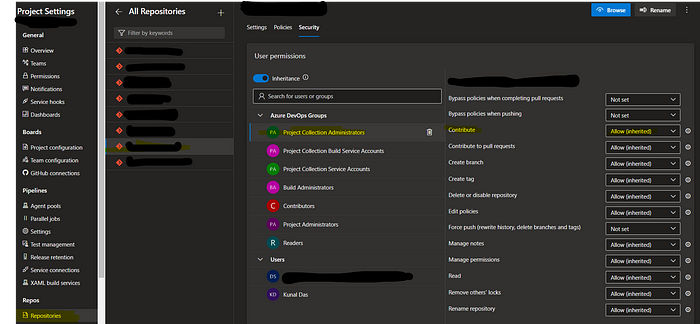
This setting essentially allows pushing from the build pipeline to the repo.
also, you have to check one more setting,
for the classic pipeline, select the below option.

and for YAML, add the below code before the YAML code.
variables:
system_accesstoken: $(System.AccessToken)
now add this bash task in the pipeline.
steps:
- bash: |
git config --global user.email "azuredevops@microsoft.com"
git config --global user.name "Azure DevOps"
REPO="$(System.TeamFoundationCollectionUri)$(System.TeamProject)/_git/$(Build.Repository.Name)"
EXTRAHEADER="Authorization: Bearer $(System.AccessToken)"
git -c http.extraheader="$EXTRAHEADER" clone $REPO
cd $(Build.Repository.Name)
mkdir 'QA-env'
cd 'QA-env'
cp '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/ARM/TemplateForWorkspace.json' .
cp '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/ARM/TemplateParametersForWorkspace.json' .
cd ..
git add Template-QA/TemplateForWorkspace.json
git add Template-QA/TemplateParametersForWorkspace.json
MAINBRANCHNAME=main
git config http.$REPO.extraHeader "$EXTRAHEADER"
git commit -a -m "added QA json updated files"
echo -- Merge $(Build.SourceBranchName) to $MAINBRANCHNAME --
git fetch origin $(Build.SourceBranchName) --prune
git merge origin/$(Build.SourceBranchName) -m "merge $(Build.SourceBranchName) to $MAINBRANCHNAME" --no-ff --allow-unrelated-histories
git push origin $MAINBRANCHNAME
git push origin --tags
displayName: 'Bash Script'
If you are using a classic pipeline add a bash task
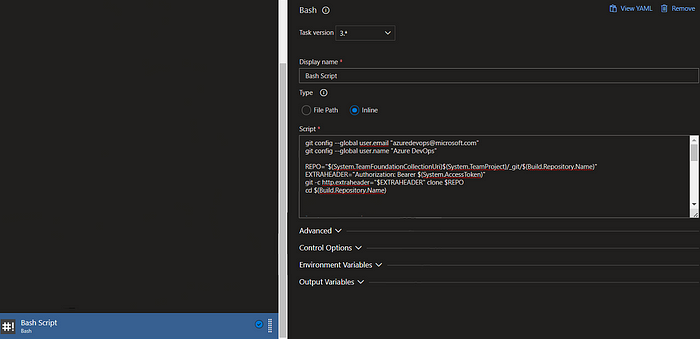
And add the below script as inline,
git config --global user.email "azuredevops@microsoft.com"
git config --global user.name "Azure DevOps"
REPO="$(System.TeamFoundationCollectionUri)$(System.TeamProject)/_git/$(Build.Repository.Name)"
EXTRAHEADER="Authorization: Bearer $(System.AccessToken)"
git -c http.extraheader="$EXTRAHEADER" clone $REPO
cd $(Build.Repository.Name)
mkdir 'qa1-ause-asy-01'
cd 'qa1-ause-asy-01'
cp '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/_Synapse-CI-pipeline/drop/ARM/TemplateForWorkspace.json' .
cp '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/_Synapse-CI-pipeline/drop/ARM/TemplateParametersForWorkspace.json' .
cd ..
git add Template-QA/TemplateForWorkspace.json
git add Template-QA/TemplateParametersForWorkspace.json
MAINBRANCHNAME=main
git config http.$REPO.extraHeader "$EXTRAHEADER"
git commit -a -m "added QA json updated files"
echo -- Merge $(Build.SourceBranchName) to $MAINBRANCHNAME --
git fetch origin $(Build.SourceBranchName) --prune
git merge origin/$(Build.SourceBranchName) -m "merge $(Build.SourceBranchName) to $MAINBRANCHNAME" --no-ff --allow-unrelated-histories
git push origin $MAINBRANCHNAME
git push origin --tags
you can update the commit message according to your need,
In this script, the following actions are being performed:
- The
mkdircommand is creating a new directory calledQA-env. - The
cdcommand is changing the current working directory toQA-env. - The
cpcommand is copying the filesTemplateForWorkspace.jsonandTemplateParametersForWorkspace.jsonfrom theARMsubdirectory of the default working directory to the current working directory (QA-env). - The
cd ..command is changing the current working directory back to the parent directory. - The
git addcommand is adding the filesTemplateForWorkspace.jsonandTemplateParametersForWorkspace.jsonto the staging area in Git. This means that these files will be included in the next commit.
once done you will see the changes getting merged in the repo
That is it,
I guess you can try the steps and get back to me if any help is required!
Credit :
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/release/?view=azure-devops
https://chuvash.eu/2021/04/09/git-merge-develop-to-main-in-an-azure-devops-release/




